As tensions between India and Pakistan escalate, the economic ramifications for both nations are profound. However, Pakistan’s mounting foreign debt and reliance on international loans, particularly from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), place it in a precarious position. This blog delves into the intricacies of Pakistan’s foreign debt, its implications during the ongoing conflict, and the broader economic landscape shaped by the India-Pakistan war.Reuters+2The Guardian+2The Guardian+2
Understanding Pakistan’s Foreign Debt Landscape
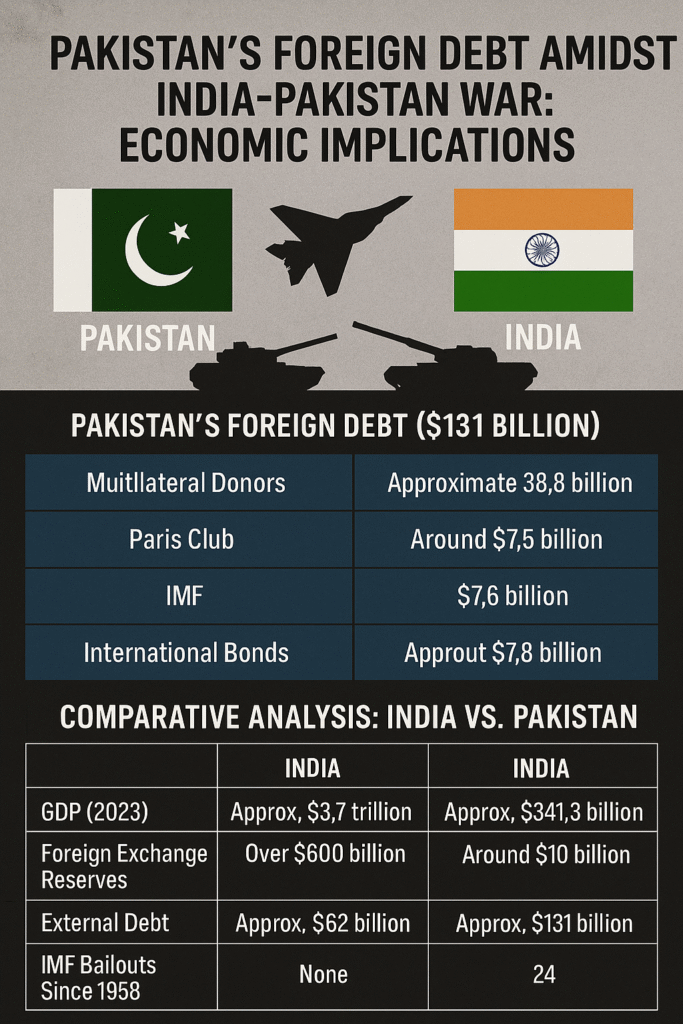
As of the fourth quarter of 2024, Pakistan’s external debt stood at approximately $131 billion . This debt is a culmination of loans from various sources:Wikipedia+3Trading Economics+3The Times of India+3
- Multilateral Donors: Approximately $38.8 billion, including institutions like the World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
- Paris Club: Around $7.5 billion owed to this group of major creditor countries.
- IMF: Outstanding loans amounting to $7.6 billion .
- International Bonds: About $7.8 billion through instruments like Eurobonds and Sukuks.IMF+2Wikipedia+2Wikipedia+2
A significant portion of this debt, over 20%, is attributed to bilateral loans from China, reflecting the deep financial ties between the two nations .
IMF’s Role in Pakistan’s Economic Stability
Pakistan’s relationship with the IMF has been longstanding, with the country entering its 24th bailout program in 2024 . The most recent agreement, approved in September 2024, entailed a $7 billion loan under a 37-month Extended Fund Facility . This infusion was crucial in averting a potential default and stabilizing the nation’s dwindling foreign exchange reserves, which hovered around $10 billion, barely sufficient to cover three months of imports .ORF OnlineORF Online+3Wikipedia+3IMF+3The Times of India
However, the IMF’s assistance comes with stringent conditions, including fiscal austerity measures, subsidy reductions, and structural reforms. These stipulations often lead to public discontent and pose challenges for successive governments in implementing long-term economic strategies.
The Economic Strain of the India-Pakistan Conflict
The recent escalation in hostilities, marked by airstrikes and artillery exchanges, has exacerbated Pakistan’s economic vulnerabilities. The conflict’s immediate impacts include:The Guardian+2AP News+2Reuters+2The Guardian+7Reuters+7Reuters+7
- Currency Depreciation: The Pakistani rupee has faced downward pressure, mirroring the Indian rupee’s decline amid market uncertainties .
- Trade Disruptions: Border closures and heightened security have hampered trade routes, affecting exports and imports.
- Investor Confidence: The volatile security situation deters foreign investment, crucial for economic growth.Reuters+2Reuters+2Reuters+2
Moody’s has highlighted that prolonged tensions could derail Pakistan’s fiscal recovery, emphasizing the need for diplomatic resolutions to prevent further economic deterioration .Reuters+1ETBFSI.com+1
Comparative Analysis: India vs. Pakistan’s Economic Resilience
While both nations bear the brunt of conflict-induced economic challenges, their capacities to absorb shocks differ:
| Aspect | India | Pakistan |
|---|---|---|
| GDP (2023) | Approx. $3.7 trillion | Approx. $341.3 billion |
| Foreign Exchange Reserves | Over $600 billion | Around $10 billion |
| External Debt | Approx. $620 billion | Approx. $131 billion |
| IMF Bailouts Since 1958 | None | 24 |
India’s diversified economy and substantial reserves provide a buffer against prolonged conflicts, whereas Pakistan’s limited fiscal space and dependency on external aid amplify its economic fragility.
The Path Forward: Navigating Economic Recovery
For Pakistan to achieve sustainable economic stability, several measures are imperative:
- Structural Reforms: Implementing comprehensive reforms to enhance tax collection, reduce fiscal deficits, and improve governance.
- Diversifying the Economy: Investing in sectors beyond agriculture and textiles to broaden the economic base.
- Strengthening Institutions: Enhancing the capacity and transparency of financial institutions to build investor confidence.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Prioritizing peaceful resolutions to conflicts to ensure a conducive environment for economic growth.
Conclusion
The intertwining of Pakistan’s foreign debt challenges with the ongoing India-Pakistan conflict underscores the urgency for strategic economic planning and diplomatic initiatives. Addressing the root causes of financial instability and fostering regional peace are pivotal for Pakistan to navigate its current economic quagmire and pave the way for a resilient future.
